오늘할일
- props & state & event 이용해 WEB 링크를 클릭하면 welcome모드가 나오도록 만들기

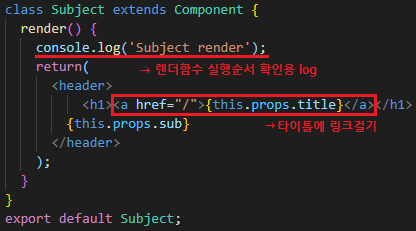
Subject.js - <h1>타이틀에 링크걸기
**코드보기(복사용 첨부 / 더보기클릭)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Subject extends Component {
render() {
console.log('Subject render');
return(
<header>
<h1><a href="/">{this.props.title}</a></h1>
{this.props.sub}
</header>
);
}
}
export default Subject;
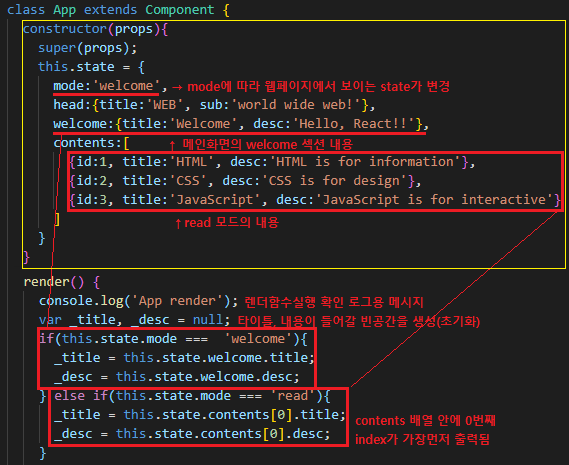
App.js - state 추가하기
"state를 바꾸면 js가 다시 실행되며 웹페이지가 리로드된다. 모든 js파일의 render함수가 다 실행됨.
다시 말하면 props의 state가 바뀌면 화면이 다시 그려진다."
리액트에서 state값이 바뀌면 해당되는 컴포넌트의 렌더함수가 호출되도록 약속되어있다.
그래서 그 안에 들어있는 하위컴포넌트들이 가진 새끼 render() 함수들도 줄줄이 재호출이 된다.
- constructor()의 state에 웰컴모드와 내용을 추가한다.
mode:'welcome',
welcome:{title:'Welcome', desc:'Hello, React!!'},
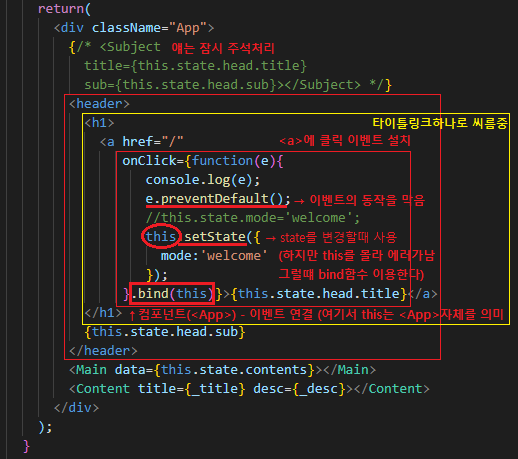
App.js - event 추가하기
onClick()={function(){}} 형식을 사용하여 이벤트 설치를 해보자.
- 온클릭 핸들러메소드로 이벤트를 실행하면 항상 리로드가 된다. 리액트의 큰 장점은 리로드없이 페이지 로딩하는 건데 이건 뭥미?
→ 이럴 땐 핸들러메소드 인자를 e로 주고 e.preventDefault(); 을 사용해보자 (리로드X 이벤트동작X)
**e.preventDefault 란? 그리고 vs e.stopPropagation (설명첨부)
a 태그나 submit 태그는 고유의 동작이 있다. 페이지를 이동시킨다거나 form 안에 있는 input 등을 전송한다던가 그러한 동작이 있는데 e.preventDefault 는 그 동작을 중단시킨다.
e.stopPropagation는 이벤트가 상위 엘리먼트에 전달되지 않게 막아 준다.
- state값을 변경할때는 setState() 를 반드시 사용한다. 그래야 리액트가 변경사항을 알기 때문이다.
BAD this.state.mode='welcome'; → 리액트 입장에서는 몰래바꾼셈이다. 값이 바뀌었는지모르니깐 렌더링이 안된다.
GOOD this.setState({mode:'welcome'}); → setState 함수를 사용하면 리액트가 그제서야 알게된다.
- setState와 함께 bind(this로 지정할 변수) 함수를 사용하면 → 괄호안의 변수가 this가 된다.
this를 찾을 수 없어서 에러가 발생하면 함수에 bind(this)를 추가해주면된다.
**코드보기(복사용 첨부 / 더보기클릭)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Subject from "./components/Subject.js";
import Main from "./components/Main.js";
import Content from "./components/Content.js";
import './App.css';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
mode:'welcome',
head:{title:'WEB', sub:'world wide web!'},
welcome:{title:'Welcome', desc:'Hello, React!!'},
contents:[
{id:1, title:'HTML', desc:'HTML is for information'},
{id:2, title:'CSS', desc:'CSS is for design'},
{id:3, title:'JavaScript', desc:'JavaScript is for interactive'}
]
}
}
render() {
console.log('App render');
var _title, _desc = null;
if(this.state.mode === 'welcome'){
_title = this.state.welcome.title;
_desc = this.state.welcome.desc;
} else if(this.state.mode === 'read'){
_title = this.state.contents[0].title;
_desc = this.state.contents[0].desc;
}
return(
<div className="App">
{/* <Subject
title={this.state.head.title}
sub={this.state.head.sub}></Subject> */}
<header>
<h1>
<a href="/"
onClick={function(e){
console.log(e);
e.preventDefault();
//this.state.mode='welcome';
this.setState({
mode:'welcome'
});
}.bind(this)}>{this.state.head.title}</a>
</h1>
{this.state.head.sub}
</header>
<Main data={this.state.contents}></Main>
<Content title={_title} desc={_desc}></Content>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
**state와 setState란? (설명첨부)
state는 렌더링 결과물(화면상)에 영향을 주는 정보이다. state를 이용해 data에 변화를 줄 수 있다.
setState()는 비동기이며(리로드 매번 안해도 된다는 의미), 컴포넌트의 state 객체에 대한 업데이트를 실행한다.
state가 변경되면, 컴포넌트는 리렌더링(새로고침)된다. setState() 함수를 사용하면 state를 업데이트하더라도 즉시 반영되지 않는다.
setState(변경할 값, callback함수)
- 첫 번째 인수로 전달된 state와 prop는 가장 최신의 값이다.
- 두 번째 인수 callback은 setState의 실행이 완료 후 컴포넌트가 렌더링 후에(다끝나고) → 그 담에 실행될 함수입니다. (생략가능)
'React' 카테고리의 다른 글
| React(12) 컴포넌트 이벤트 만들기 (0) | 2021.01.05 |
|---|---|
| React(11) bind()함수 이해하기 (0) | 2021.01.04 |
| React 실행 오류 out of memory / Render process gone (4) | 2021.01.04 |
| React(9) State로 내용구현하기 (0) | 2021.01.02 |
| React(8) Component파일 분리하기 (0) | 2021.01.01 |



댓글